
For example, a company might have 60-day terms for money owed to their supplier, which results in requiring their customers to pay within a 30-day term. Current liabilities can also be settled by creating a new current liability, such as a new short-term debt obligation. As you continue to grow and expand your business, you’re likely going to take on more debt as you go.

Balance Sheets 101: What Goes On a Balance Sheet?
- When the company pays its balance due to suppliers, it debits accounts payable and credits cash for $10 million.
- Liabilities generally cause some form of restriction on a business’s operations.
- Short-term debt is typically the total of debt payments owed within the next year.
- However, if the number is too high, it could mean the company is not leveraging its assets as well as it otherwise could be.
- Understanding what liabilities are in accounting, as well as the most common examples of each type, can help you track and identify them in your balance sheet.
Please refer to the Payment & Financial Aid page for further information. The left side of the balance sheet is the business itself, including the buildings, inventory for sale, and cash from selling goods. If you were to take a clipboard and record everything you found in a company, you would end up with a list that looks remarkably like the left side of the balance sheet. That said, if the lawsuit isn’t successful, then your business would not have any liability. A contingent liability only gets recorded on your balance sheet if the liability is probable to happen.

The most important equation in all of accounting
- Liabilities are categorized as current or non-current depending on their temporality.
- Here is a list of some of the most common examples of current liabilities.
- Overall, liabilities will almost always require future payments depending on the agreement between you and the other party involved.
- They represent obligations or debts that a business owes to other parties, such as suppliers, lenders, and employees.
- If you made an agreement to pay a third party a sum of money at a later date, that is a liability.
- If you have a debt ratio of 60% or higher, investors and lenders might see that as a sign that your business has too much debt.
He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. Our article about accounting basics discusses in detail the concepts you need to understand small business accounting. Expenses are internal because they involve costs by the company during business transactions.
What Is Financial Ratio Analysis? A Small Business Guide
Below is a current liabilities example using the consolidated balance sheet of Macy’s Inc. (M) from the company’s 10-Q report reported on Aug. 3, 2019. We accept payments via credit card, wire transfer, Western Union, and (when available) bank loan. Some candidates may qualify for scholarships or financial aid, which will be credited against the Program Fee once eligibility is determined.
How do liabilities affect a business’s current and long-term operations?
This is often used as operating capital for day-to-day operations by a company of this size rather than funding larger items which would be better suited using long-term debt. An expense is the cost of operations that a company incurs to generate revenue. Any liability that’s not near-term falls under non-current liabilities that are expected to be paid in 12 months or more. Long-term debt is also known as bonds payable and it’s usually the largest liability and at the top of the list. Liabilities also have implications for a company’s cash flow statement, as they may directly influence cash inflows and outflows. For example, a mortgage payable impacts both the financing and investing sections of the cash flow statement.

Unlike liabilities, equity is not a fixed amount with a fixed interest rate. Everything listed is an item that the company has control over and can use to run the business. The accounting equation is the mathematical structure of the balance sheet. Liabilities in financial accounting need not be legally enforceable; but can be based on equitable obligations or constructive obligations.
- It falls under the category of things you owe or borrow, including short-term loans and long-term loans.
- If you were to take a clipboard and record everything you found in a company, you would end up with a list that looks remarkably like the left side of the balance sheet.
- Once the utilities are used, the company owes the utility company.
- The higher it is, the more leveraged it is, and the more liability risk it has.
- Here’s how to calculate the current ratio, a financial metric that measures your company’s ability to pay off its short-term debts.
This is why it’s critical to understand the differences between current and long-term liabilities. Plus, making sure that they get recorded properly on your balance sheet is just as important. The long-term debt ratio is a concept similar to the short-term debt ratio. The only difference is that current liabilities are not included in the equation.
Current vs. non-current liabilities
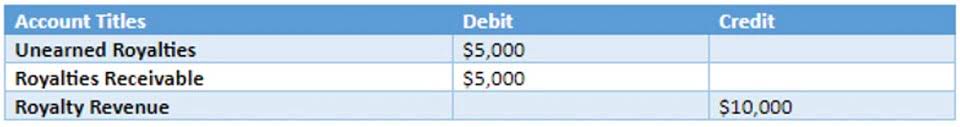
As you can see with Amrish’s art gallery, due to a lower level of equities, the debt-to-capital ratio is rather high. If it is expected to be settled in the short-term (normally within 1 year), then it is a current liability. Unearned Revenue – Unearned revenue is slightly different from other liabilities because it doesn’t involve direct borrowing.
Why Are Liabilities Important to Small Business?
They’re any debts or obligations that your business has incurred that are due in over a year. Businesses will take on long-term debt to acquire new capital to purchase capital assets or invest in new capital projects. Basically, these are any debts or obligations you have that need to get paid within a year. It’s important to keep a what falls under liabilities in accounting close eye on your current liabilities to help make sure that you have enough liquidity from your current assets. This is to help guarantee that any debts or obligations your business has can get met. Current liabilities are obligations that a company needs to settle within a year, whereas long-term liabilities extend beyond a year.
How are liabilities used in calculating a company’s net worth?
- It shows investors and analysts whether a company has enough current assets on its balance sheet to satisfy or pay off its current debt and other payables.
- Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance.
- Financial liabilities can be either long-term or short-term depending on whether you’ll be paying them off within a year.
- Get up and running with free payroll setup, and enjoy free expert support.
- Besides these two primary categories, contingent liabilities and other specific cases may also exist, further adding complexity to accounting practices.
An operating cycle, also referred to as the cash conversion cycle, is the time it takes a company to purchase inventory and convert it to cash from sales. An example of a current liability is money owed to suppliers in the form of accounts payable. In the world of accounting, a liability refers to a company’s financial obligations or debts that arise during the course of business operations. These are obligations owed to other entities, which must be fulfilled in the future, usually by transferring assets or providing services. Liabilities play a crucial role in a company’s financial health, as they fund business operations and impact the company’s overall solvency. Analysts and creditors often use the current ratio, which measures a company’s ability to pay its short-term financial debts or obligations.
